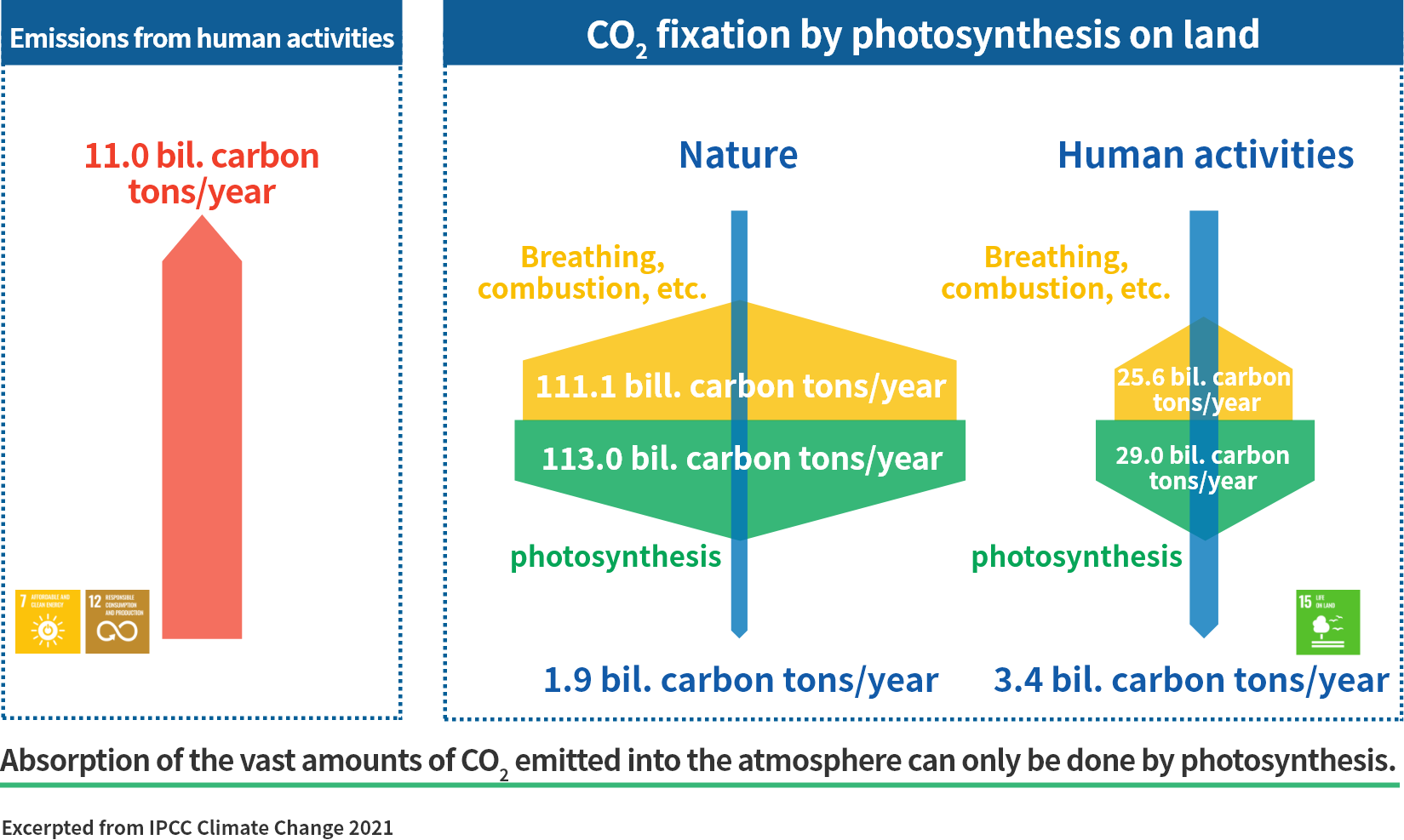
The amount of CO₂ emitted by humans annually is estimated to be 11 billion tons carbon equivalent. On the other hand, CO₂ fixed by photosynthesis on land is estimated to be 113 billion carbon tons in nature, and 29 billion carbon tons by agriculture, forestry and other human activities. Most of these amounts ends up being of course released again through breathing and combustion, but it is estimated that 1.9 billion carbon tons is permanently fixed in the natural world and 3.4 billion carbon tons by agriculture, forestry and the like. While various technologies have been proposed for absorption of CO₂ in the atmosphere, photosynthesis remains the only means for absorbing the huge amount of CO₂ being emitted.
Realizing a Carbon-Negative Society through Carbon Cultivation
Carbon negativity can only be achieved by increasing carbon fixation through agriculture and forestry, using the resulting biomass-derived fuels to reduce emissions of CO₂ from fossil resources, and reducing biomass-derived CO₂ generation through conversion to materials and carbon capture and storage. This hub will challenge the limits of carbon negativity by means of carbon cultivation, making maximum use of the potential of photosynthesis.
Carbon cultivation reduces carbon emissions and store carbon. We will create new biomass industries in agriculture, forestry, and fisheries to replace fossil-resource-dependent industries. Rice cultivation will activate the local economy while suppressing methane generation and promoting carbon storage. Increased rice production will also contribute to food security.
In forestry, carbon cultivation using fast-growing trees will increase carbon storage. A regional biomass industry cluster will be created by, for example, using materials produced through carbon cultivation as an alternative to plastic. Healthy forests will also lead to disaster prevention and mitigation.
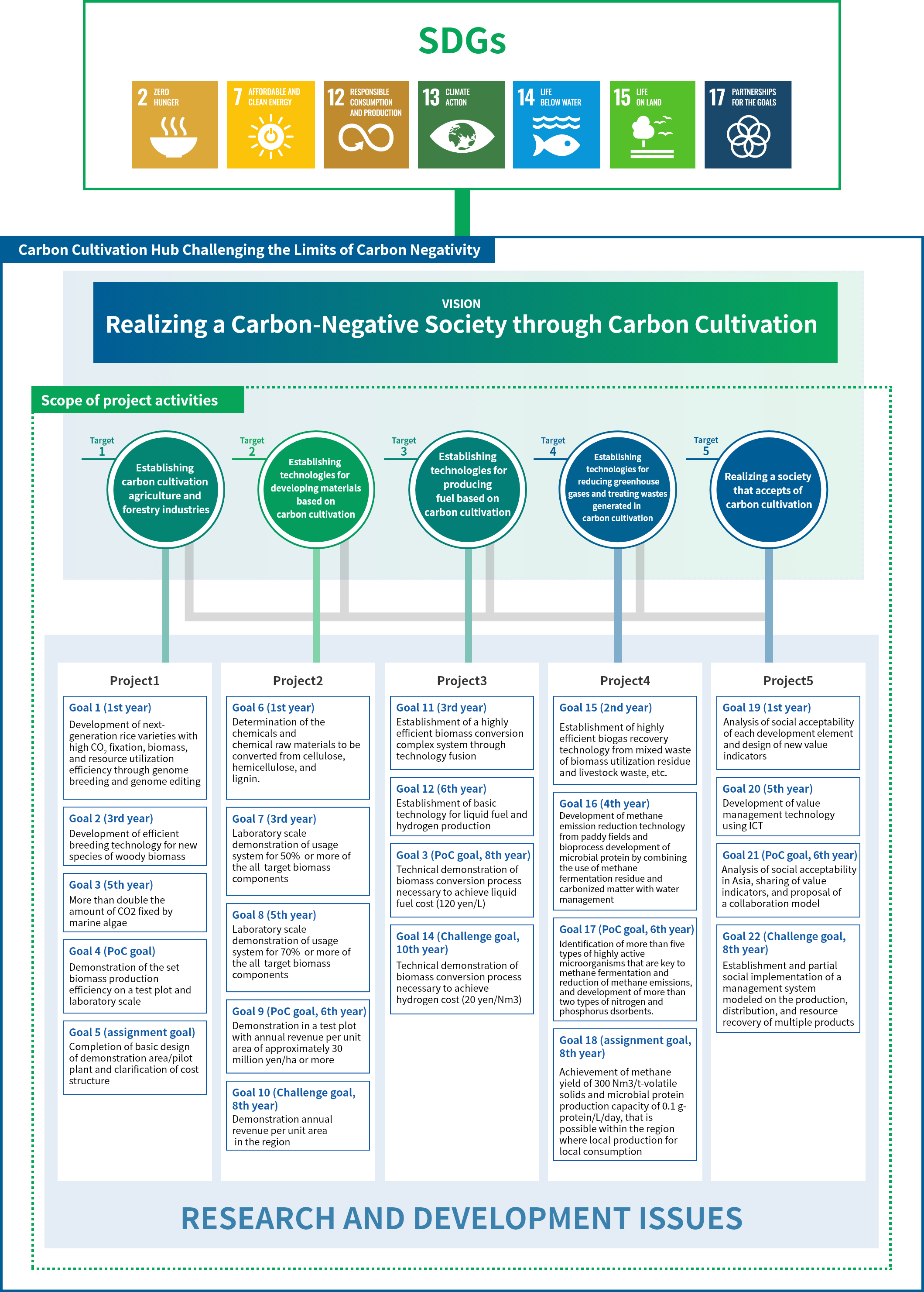
To realize this vision, we have set the following five targets:
1: Establishing carbon cultivation agriculture and forestry industries
2: Establishing technologies for developing materials based on carbon cultivation
3: Establishing technologies for producing fuel based on carbon cultivation
4: Establishing technologies for reducing greenhouse gases and treating wastes generated in carbon cultivation
5: Realizing a society that accepts carbon cultivation
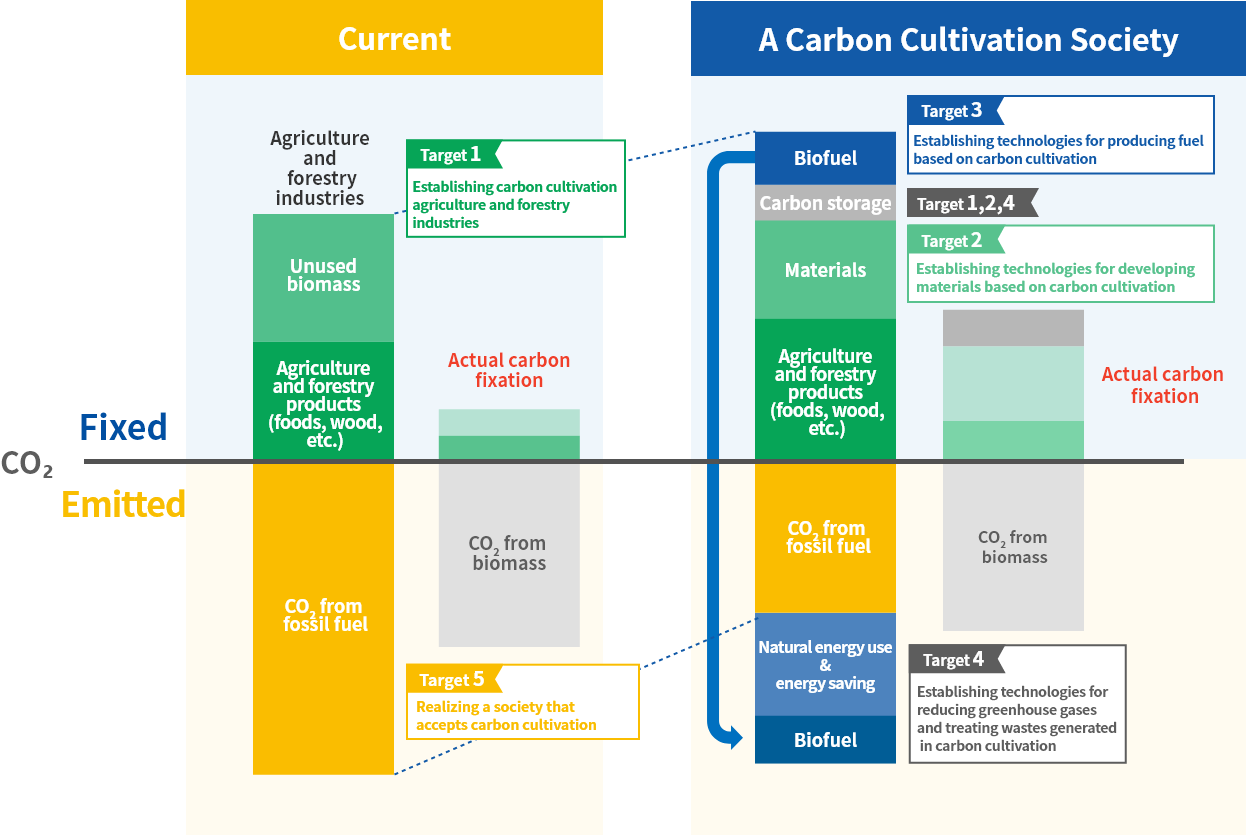
The positioning of each target is illustrated in the diagram below.
Carbon fixed by photosynthesis in rice, trees, and algae is used as material and fuel, and unused biomass is processed and used as fertilizer, while excess carbon is stored. Measures will be devised for gaining public acceptance of this cycle and implementing it. Since achieving this cycle will require social implementation at each stage, various companies will participate in the social implementation processes.
Based on these targets, we have set the following five research themes:
1: Development of sustainable carbon cultivation technology
2: Development of carbon cultivation-based materials development technology
3: Development of carbon cultivation-based technologies for producing fuel
4: Development of technologies for reducing greenhouse gases and treating wastes generated in carbon cultivation
5: Development of evaluation methods for social acceptability